大鼠神经胶质瘤细胞C6
发表时间:2025-07-15大鼠神经胶质瘤细胞C6
一、细胞来源
1.诱导模型:大鼠神经胶质瘤细胞C6细胞系于20世纪60年代末通过化学致癌剂 N-亚硝基甲基脲(N-nitrosomethylurea) 诱导Wistar-Furth大鼠脑胶质瘤获得,具有明确的胶质瘤病理特征[1][2]。
2.细胞类型:源于星形胶质细胞,表达胶质特异性标志物S-100蛋白,其含量在静止期细胞中显著高于增殖期[1]。
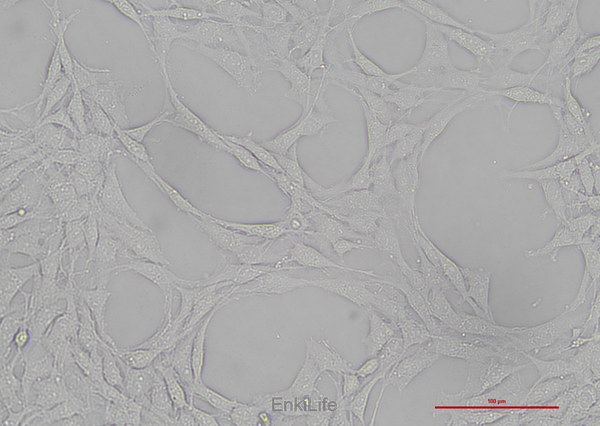
二、生物学特性
1. 形态学特征:与人类多形性胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)相似,呈高度侵袭性生长,可沿神经纤维和血管迁移[2]。细胞形态为成纤维细胞样,贴壁生长[3]。
2. 分子标志物:
- 表达 胰岛素样生长因子I(IGF-I) ,促进肿瘤免疫逃逸;敲除IGF-I可逆转致瘤性[4]。
- 分泌 神经生长因子(NGF) ,与神经元存活和分化相关[5]。
3. 代谢特征:依赖葡萄糖转运蛋白(GLUT)和己糖激酶I介导的葡萄糖代谢,其生长速率与葡萄糖摄入量正相关[6]。
4. 干细胞特性:含癌干细胞(CSC)亚群,但CD133标记无法完全识别CSC;单细胞克隆显示多数细胞具自我更新和分化潜能[7]。
三、培养与储存
1. 培养基:低糖DMEM+10% FBS+1% P/S[3]。
2. 传代与冻存:1:3~1:4进行传代,30%基础培养基+60%FBS+10%DMSO,液氮保存[3]。
四、研究应用领域
1. 肿瘤模型构建:
- 同种异体移植:注射至大鼠脑内可形成高侵袭性、血管生成活跃的胶质瘤,模拟人类GBM的微环境[2]。
- 药物筛选平台:广泛用于抗肿瘤药物(如替莫唑胺)的疗效及机制研究[8]。
2. 分子机制研究:
- 用于探究HDAC抑制剂(如丙戊酸)对胶质细胞FGF21表达的调控[9]。
- 研究PDGFR-β信号通路在放疗抵抗中的作用[10]。
五、近几年研究进展
1. 新型抗肿瘤药物:
- 黄酮类化合物(如莫林) :通过激活caspase-3/9、上调Bax/Bcl-2比值诱导凋亡[11]。
- 中药成分(槐果碱、苦参碱) :抑制C6细胞增殖,并增强化疗药物(如顺铂)疗效[12][13]。
- 榄香烯:经ERK通路下调Bcl-2,促进线粒体凋亡[14]。
2. 免疫治疗策略:
- IGF-I反义RNA转染:使C6细胞丧失致瘤性,并激发CD8?T细胞介导的免疫应答[4]。
- 神经节苷脂衍生物(O-丁酰基GD1b) :特异性抑制胶质瘤分裂,无正常细胞毒性[15]。
六、局限性与克服方法
1. 局限性:
- 遗传异质性:长期传代导致基因组不稳定,与原始肿瘤差异增大[17]。
- CSC标记缺陷:CD133和侧群(SP)染色无法准确分离CSC亚群[17]。
- 免疫微环境差异:大鼠模型无法完全模拟人类免疫系统。
2. 克服方法:
- 基因编辑技术:利用CRISPR-Cas9构建特定基因敲除模型,优化靶向治疗研究[10]。
- 联合疗法:放疗联合PDGFR-β沉默可显著增强C6细胞放射敏感性[10]。
七、总结与展望
C6细胞系作为胶质瘤研究的“金标准”模型,在揭示肿瘤生长、侵袭和耐药机制中发挥不可替代的作用[17]。未来需进一步:
1.开发人源化模型:结合患者来源异种移植(PDX),提升临床转化价值。
2.多组学整合分析:通过单细胞测序明确CSC分子特征,优化靶向策略[17]。
3.探索纳米毒性:研究二氧化钛纳米颗粒等新型材料对胶质细胞的神经毒性机制[16]。

参考文献
1. Benda P, et al. Differentiated Rat Glial Cell Strain in Tissue Culture. Science. 1968;161(3839):370-371. PMID: 4872210.
2. Grobben B, et al. Rat C6 glioma as experimental model system for the study of glioblastoma growth and invasion. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;310(3):257-270. PMID: 12457224.
3. 大鼠神经胶质瘤细胞C6说明书.武汉恩玑生命科技有限公司.
4. Trojan J, et al. Treatment and prevention of rat glioblastoma by immunogenic C6 cells expressing antisense insulin-like growth factor I RNA. Science. 1993;259(5101):94-95. PMID: 8418506.
5. Murphy RA, et al. Secretion of nerve growth factor by central nervous system glioma cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1977;72(3):769-776. PMID: 557307.
6. Nagamatsu S, et al. Rat C6 glioma cell growth is related to glucose transport and metabolism. J Neurochem. 1996;67(4):1395-1403. PMID: 8858921.
7. Shen G, et al. Identification of cancer stem-like cells in the C6 glioma cell line and the limitation of current identification methods. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(7):280-288. PMID: 18594909.
8. Stupp R, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987-992. PMID: 15758003.
9. Leng Y, et al. Valproic Acid and Other HDAC Inhibitors Upregulate FGF21 Gene Expression and Promote Process Elongation in Glia by Inhibiting HDAC2 and 7. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19(6):pyw038. PMID: 27017559.
10. Hong JD, et al. Silencing platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β enhances the radiosensitivity of C6 glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(1):119-127. PMID: 28534998.
11. Zhu S, et al. Morin Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Caspase-mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in Glioma C6 Cell Line. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1298742. PMID: 38375013.
12. 张明发, 沈雅琴. 槐果碱和氧化槐果碱抗肿瘤药理作用的研究进展. 中国药理学通报. 2020;36(3):297-3010. PMID: 322767811.
13. 张明发, 沈雅琴. 苦参碱和氧化苦参碱对神经细胞瘤抑制作用的研究进展. 中国药理学通报. 2020;36(11):1481-1484. PMID: 33146125.
14. 赵永顺. Hsp90/Raf-1及ERK通路在榄香烯诱导胶质瘤细胞凋亡中的作用. 中国中药杂志. 2011;36(7):922-922. PMID: 21837941.
15. Nieto-Sampedro M, et al. Inhibitors of Glioma Growth that Reveal the Tumour to the Immune System. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28551. PMID: 22174822.
16. Zhang X, et al. Neurotoxicity of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review. Environ Sci Nano. 2023;10(12):3243-3261. PMID: 37936811.
17. Giakoumetsis D, et al. C6 cell line: the gold standard in glioma research. Oncol Lett. 2018;16(1):41-51. PMID: 29928402.




