人正常肺上皮细胞BEAS-2B
发表时间:2025-07-23人正常肺上皮细胞BEAS-2B
一. 细胞来源
1.建系背景:BEAS-2B细胞系于1988年由Curtis C. Harris团队建立,源自非癌个体的人正常支气管上皮细胞,通过腺病毒12-SV40杂交病毒转染实现永生化,保留非致瘤性特征 [1][2][3]。
2.争议点:近年研究发现其可能兼具间充质干细胞(MSC)特性,挑战了传统上皮细胞起源认知[1]。
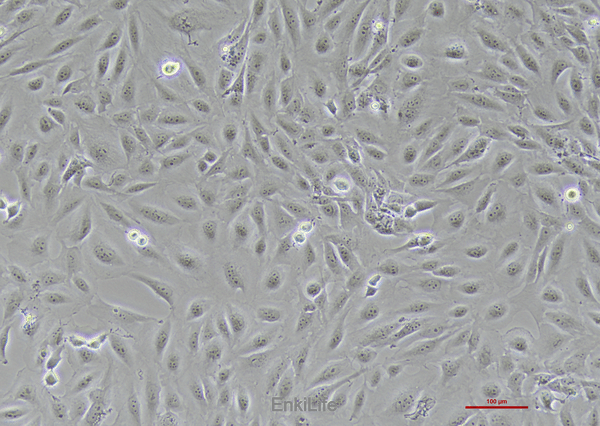
二. 生物学特性
1.形态与分子标志物:
- 典型上皮形态,表达角蛋白CK8/CK18和E-钙黏蛋白(E-Cadherin) [3][15]。同时表达MSC表面标志物(如CD73、CD90、CD105),并具多向分化潜能(成骨、成脂)[1]。
2.功能特性:
- 免疫调节:抑制T淋巴细胞增殖及Th1分化,诱导IDO1表达 [1]。
- 代谢特征:糖酵解和氧消耗受培养条件显著影响(如胎牛血清FBS)[4]。
3.争议特性:
- 缺乏分化能力(如气液界面培养中无法形成紧密连接或纤毛/杯状细胞) [15],但部分研究支持其MSC特性非上皮-间质转化(EMT)所致[1]。
三. 培养与储存
1.培养条件:基础培养基为DMEM/F12,需添加生长因子(如EGF、胰岛素)。
2.关键影响因素:胎牛血清(FBS)显著改变细胞代谢和砷毒性敏感性,需谨慎选择培养体系 [4]。
3.储存:液氮冻存(含10% DMSO+90% FBS),复苏存活率>90%。
四. 研究应用领域
1.呼吸毒理学:
- 评估环境污染物(如砷、石棉、PM2.5)的细胞毒性及致癌机制[5][6][7]。
2.肺癌研究:
- 作为非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的对照细胞,研究致癌基因(如circ-0067934、miR-21)的表达差异[8][9]。
- 慢性砷暴露模型显示致癌信号通路(如STAT3-Akt)激活[10][16]。
3.免疫与感染:高基础干扰素刺激基因(ISG)表达赋予甲型流感病毒抗性[11]。
真菌感染应答机制研究 [12]。
五. 近年研究进展(2020–2025)
1.MSC特性证实:2020年研究明确其表达MSC标志物,具免疫抑制功能,为肺部纤维化疾病研究提供新模型 [1]。
2.代谢模型优化:计算模型整合氧/葡萄糖代谢参数,提升体外毒性预测准确性 [13]。
3.致癌机制深化:
- 砷暴露通过NFAT通路诱导COX-2表达,抑制凋亡 [14]。
- p53缺失增强恶性转化能力(软琼脂克隆、裸鼠致瘤) [10]。
六. 局限性与克服方法
1.局限性:
- 表型不稳定性:FBS诱导代谢和基因表达偏移,影响实验可重复性 [4]。
- 分化缺陷:无法模拟气道上皮屏障功能,限制呼吸生理研究 [15]。
2.克服策略:
- 优化无血清培养体系,减少批次差异 [4]。
- 联合原代细胞或类器官模型验证关键结论 [13。
七. 总结与展望
BEAS-2B细胞因其易获取、永生化特性,成为呼吸疾病研究的核心工具。未来研究方向可:
1.深入解析其上皮/MSC双重特性的分子基础;
2.开发标准化培养方案以提升数据可比性;
3.整合多组学技术探索其在精准毒理学中的应用。

参考文献
1. Human Lung Epithelial BEAS-2B Cells Exhibit Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Han X, et al. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227175. [PMID: 31940397]
2. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus. Reddel RR, et al. Cancer Res. 1988;48(7):1904-1903. [PMID: 2832044]
3. Human cell-based in vitro systems to assess respiratory toxicity: a case study using silanes. Sharma M, et al. Toxicol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;195(2):213-230. [PMID: 37498623]
4. Culture conditions profoundly impact phenotype in BEAS-2B, a human pulmonary epithelial model. Zhao F, et al. J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Aug;35(8):945-51. Epub 2014 Dec 19. [PMID: 25524072]
5. Genome-wide analysis of BEAS-2B cells exposed to trivalent arsenicals. Chilakapati J, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;247(1):23-29. [PMID: 205620211]
6. 张敏.温石棉和石棉替代品致BEAS-2B和Met-5A细胞的损伤作用[D].浙江大学,2013.
7. 武博.鸭舍环境微生物气溶胶监测及其对小鼠肺损伤与BEAS-2B细胞毒理机制的研究[D].山东农业大学,2020.
8. Overexpression of circ-0067934 is associated with increased cellular proliferation and the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Zou Q, et al. Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5551-5556. [PMID: 30344708]
9. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. Xu LF, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Aug 1;9(8):e103698. [PMID: 25084400]
10. Human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells, an appropriate in vitro model to study heavy metals induced carcinogenesis. Park YH, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;287(3):240-5. [PMID: 26091798]
11. High basal expression of interferon-stimulated genes in human bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells contributes to influenza A virus resistance. Seng LG, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 14;9(10):e109023. [PMID: 25313647]
12. In silico model development and optimization of in vitro lung cell population growth. Mostofinejad A, et al. PLoS One. 2024 May 15;19(5):e0300902. [PMID: 38748626]
13. Cyclooxygenase-2 induction by arsenite is through a nuclear factor of activated T-cell-dependent pathway and plays an antiapoptotic role in Beas-2B cells. Ding J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 25;281(34):24405-13. [PMID: 16809336]
14. Evaluation of Differentiated Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Culture Systems for Asthma Research. Stewart CE, et al. J Allergy. 2012;2012:943984. [PMID: 22287916]
15. Chronic occupational exposure to arsenic induces carcinogenic gene signaling networks and neoplastic transformation in human lung epithelial cells. Stueckle TA, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 1;261(2):204-16. [PMID: 22521957]




